Nucleic Acids
Abstract
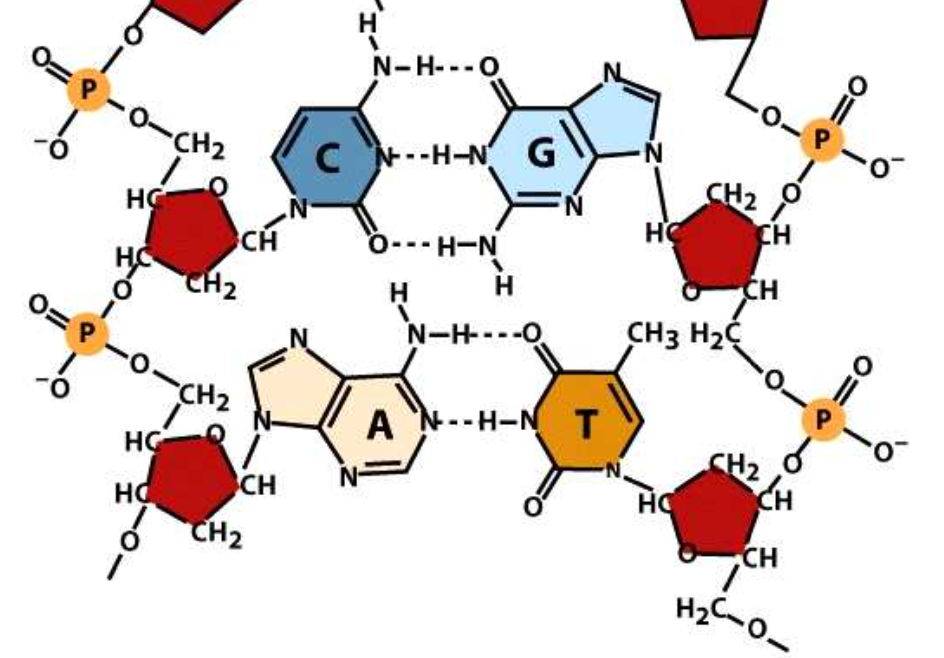
DNA consists of two antiparallel complementary base-paired strands. DNA is composed of four different types of bases: the purines adenine and guanine (composed of two-ringed structures) and the pyrimidines cytosine and thymine (single-ringed structures) The complementary strands of DNA allow one strand to be used as a template for replication. Similarly, one strand of DNA is used as a template for the synthesis of RNA in transcription. The double helical DNA is a stable molecule; several important intermolecular forces are involved in maintaining its stability. The sequence of RNA is translated into protein; thus the amino acid sequence of a protein is prescribed by the sequence of bases in the DNA. The amino acid sequence of a protein is an important determinant of protein structure, which is linked to the function of the protein. Thus the structure of the DNA specifies the characteristics of an organism.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright of this work and the permissions granted to users of the PAC are defined in the PAC Activity User License.

