What makes a good buffer?
Abstract
Learning Objectives
- Describe the relationship between pH, Ka and [A-]/[HA] for a buffer solution.
- Use logarithmic relationships to convert the equilibrium expression into the Henderson Hasselbalch (HH) equation, and use both equations for pH calculations.
- Apply the HH equation to designing a buffer for a desired pH.
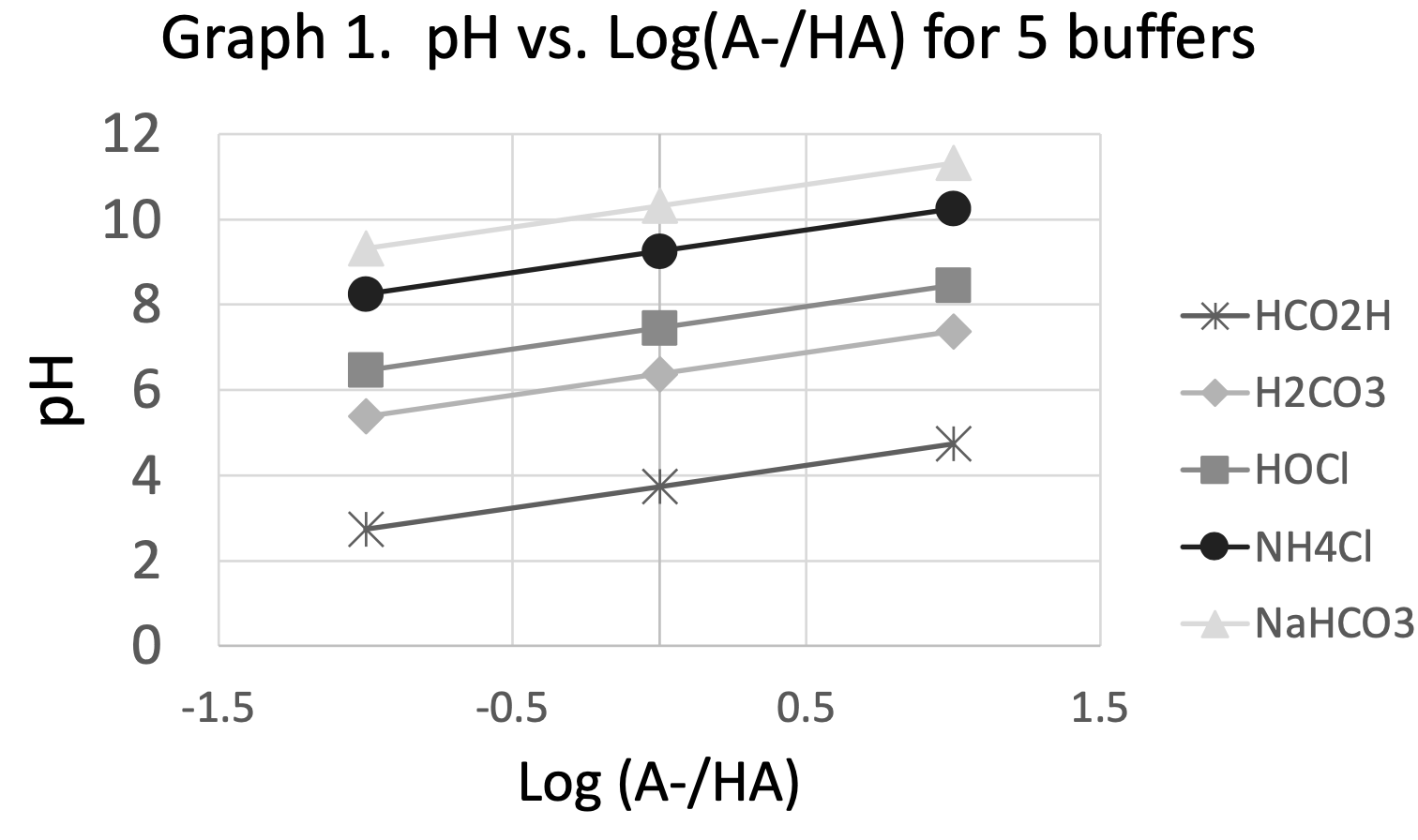
This activity uses phosphate buffer to explore the relationships between pH, Ka and [A-]/[HA]. Students use logarithmic properties to determine that the HH equation is equivalent to the equilibrium expression. Finally, students choose a pH and use the HH equation to design a buffer solution.
The activity is designed for an adult biomedical workforce training program. Students have already made buffer solutions in the laboratory and made careful pH measurements. This activity offers an opportunity to understand the factors that determine the pH of a buffer solution, reinforcing the idea that both the Ka and the [A-]/[HA] ratio are important.
Level: High School, Undergraduate Setting: Classroom
Activity Type: Learning Cycle
Discipline: Chemistry
Course: GOB Chemistry
Keywords: acids, bases, buffers, Henderson Hasselbalch equation
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Michele SprengnetherCopyright of this work and the permissions granted to users of the PAC are defined in the PAC Activity User License.

