Process Memory Layout
Cybersecurity
Abstract
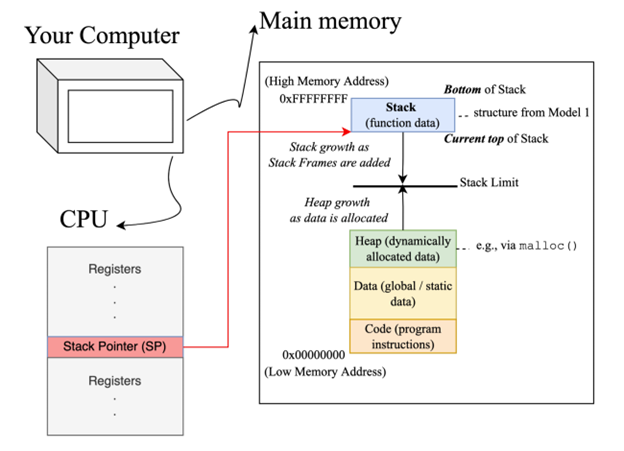
This activity aims to introduce students to the memory layout for processes that execute within a computer system. It is the second in a series of guided inquiry learning style activities that are intended to be incorporated into the Software Security module of a junior / senior level undergraduate course on Introduction to Security and Privacy. Students are expected to have completed the first activity in the series - Activity 1: Introduction to C - where they are expected to learn how to create simple C programs using variables, functions and arrays ; understand the structure of strings in C, their memory composition in bytes and the unsafe C function strcpy() ; create and run a C program that uses command-line arguments. Upon completion of the current activity, students should be able to describe the different segments within the main memory of a computer, their growth directions, and relative positions ; describe a stack pointer and program counter, what constitutes a stack frame, how and when they are added and removed from the stack and recognize the current state of the stack when given a program and the current place of execution ; and correctly identify the values of argv and argc when given a command-line input. Students are also expected to develop critical thinking and information processing skills as they work through this activity.
This activity was developed with NSF support through IUSE-1626765. You may request access to this activity via the following link: IntroCS-POGIL Activity Writing Program.
Level: Undergraduate
Setting: Classroom
Activity Type: Learning Cycle
Discipline: Computer Science
Course: Cybersecurity
Keywords: memory layout, stack, stack frame, buffer overflow, command-line parameters
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright of this work and the permissions granted to users of the PAC are defined in the PAC Activity User License.

